7.1.5.1. De-duplication
7.1.5.1.1. what is De-duplication?
De-duplication —— the process of identifying and avoiding essentially identical web pages.
In cloud computing, only a single copy of a file is stored and mutiple links to the single file are managed
With respect to web crawling, de-duplication essentially refers to the identification of identical or nearly identical web pages and indexing only a single version to return as a search result.
How can two URLs differ yet still point to the same page?
- the URL's host name can be distinct(virtual hosts)
- the URL's protocol can be distinct(http,https)
- the URL's path and/or page name can be distinct
Mirroring is the systematic replication of web pages across hosts.
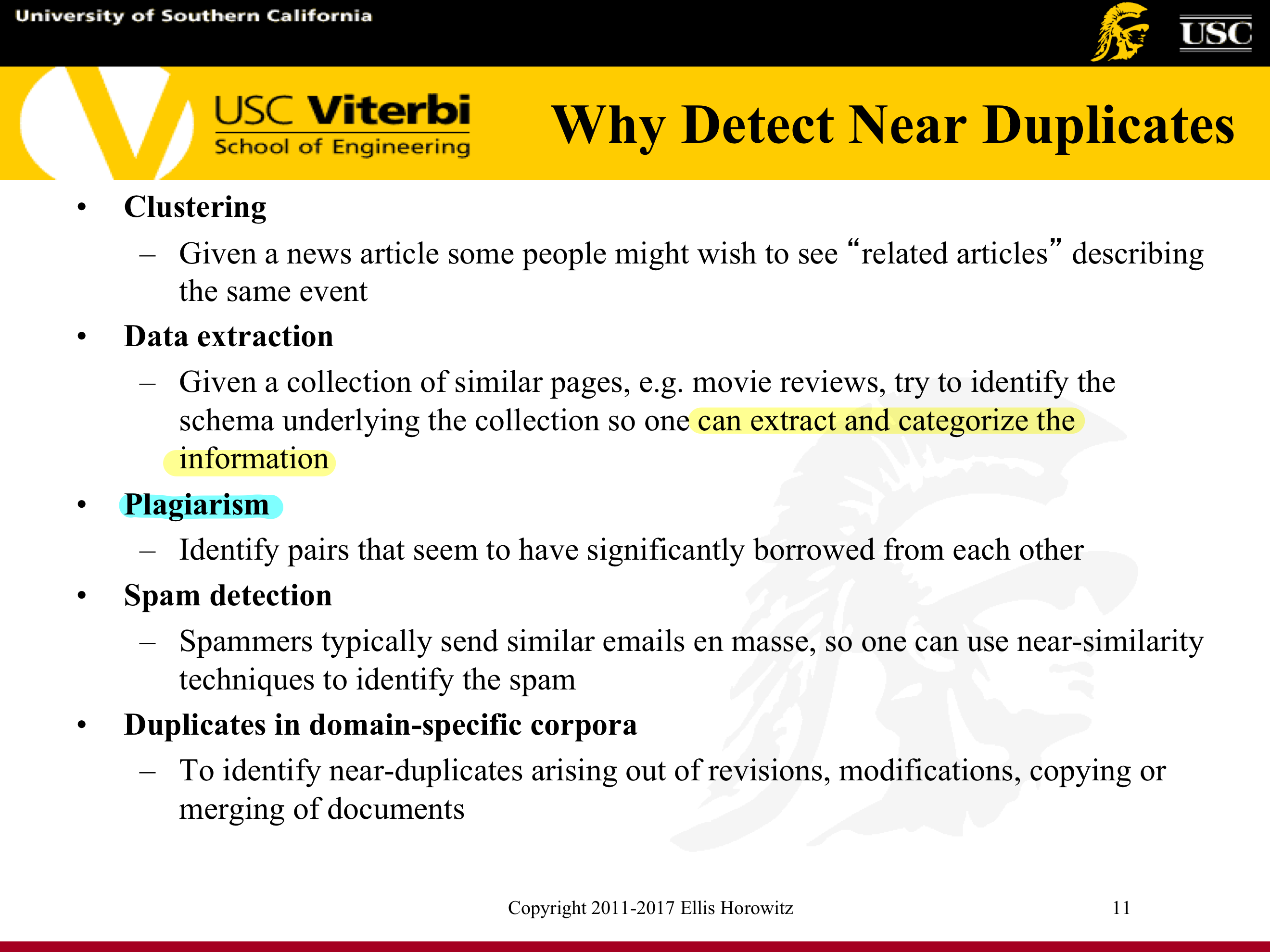
7.1.5.1.2. Why Detect Exact/Near Duplicates?

7.1.5.1.3. Solving the Duplicate/Near-Duplicate
7.1.5.1.3.1. Detection Problem
- Duplicate: Exact match
- Solution: compute fingerprints using cryptographic hashing
- SHA-1 and MD5 are the two most popular cryptographic hashing methods
- Most useful for URL matching, but also works for detecting identical web pages
- Near-Duplicate: Approximate match
- Solution: compute the syntactic similarity with an edit-distance measure, and
- Use a similarity threshold to detect near-duplicates – e.g., Similarity > 80% => Documents are “near duplicates”
7.1.5.1.3.2. Using a Cryptographic Hash Function to Convert a Web Page to a Number
A cryptographic hash function is a hash function which takes an input (or 'message') and returns a fixed-size alphanumeric string, which is called the hash value (sometimes called a message digest, digital fingerprint, digest or a checksum).
The cryptographic hash function has four main properties:
- It is extremely easy to calculate a hash for any given data.
- It is extremely computationally difficult to calculate an alphanumeric text that has a given hash.
- A small change to the text yields a totally different hash value.
- It is extremely unlikely that two slightly different messages will have the same hash.
- The MD5 message-digest algorithm is a widely used cryptographic hash function producing a 128-bit (16-byte) hash value, typically expressed in text format as a 32 digit hexadecimal number.
- The SHA-1, SHA-2 are also quite popular (160 bit, 20 byte value)
- SHA-1 was recently broken; suggestion is to now use SHA-2 family of algorithms, see – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SHA-2 • E.g. see Chrome, Settings, Advanced, https, Manage certificates, certificates, Verisign
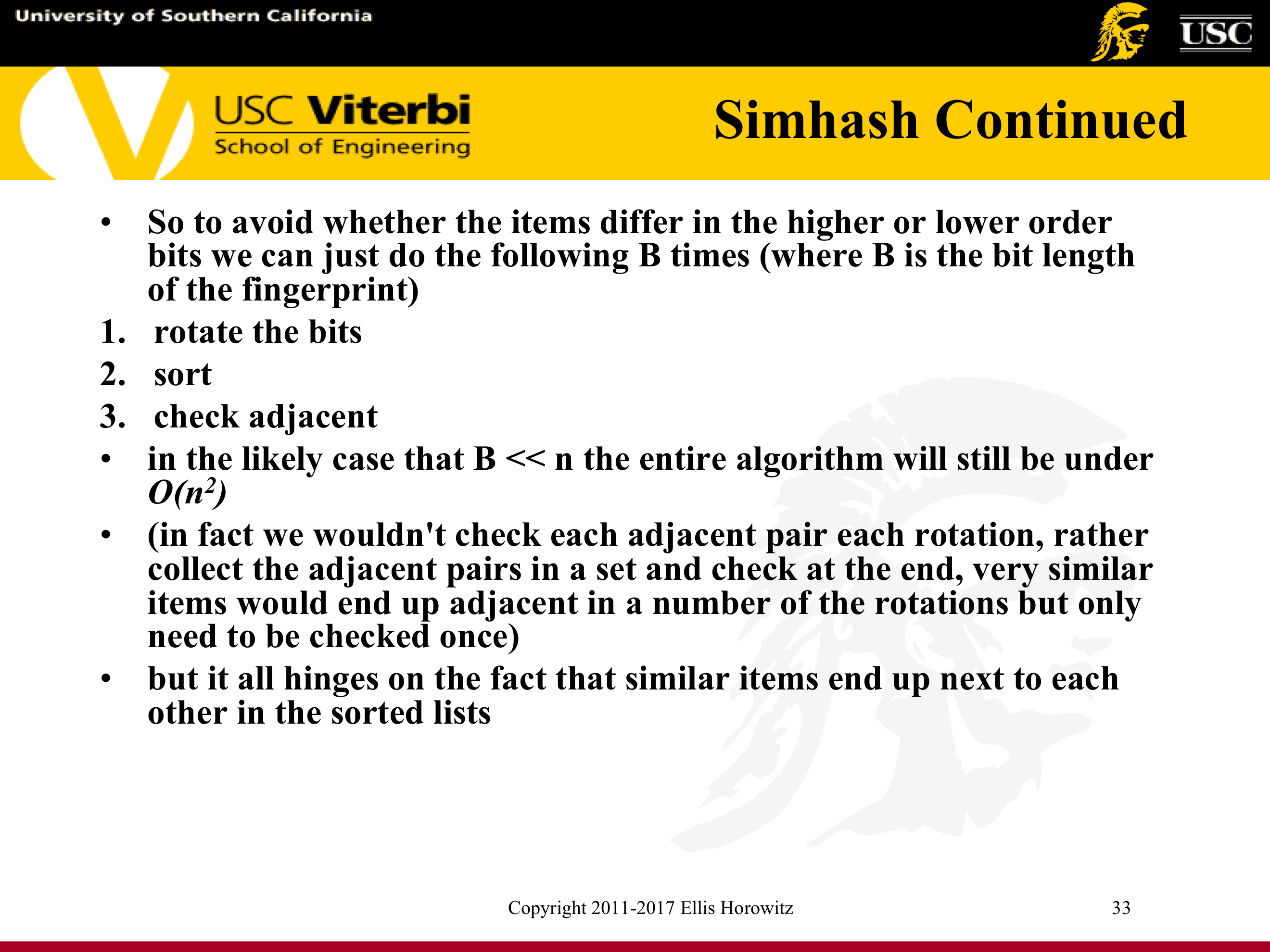
7.1.5.2. Identifying Identical Web Pages(Four Approaches)
- Compare character by character
- Hash just the first few characters and compare only those documents that hash to the same bucket
- Use a hash function that examines the entire document
- Better approach - pick some fixed random positions for all documents and make the hash function depend only on these
- Even better approach: Compute the cryptographic hash (SHA-2 or MD5) of each web page and maintain in sorted order, O(log n) to search
7.1.5.3. Identifying Near Identical Web Pages - Two Approaches
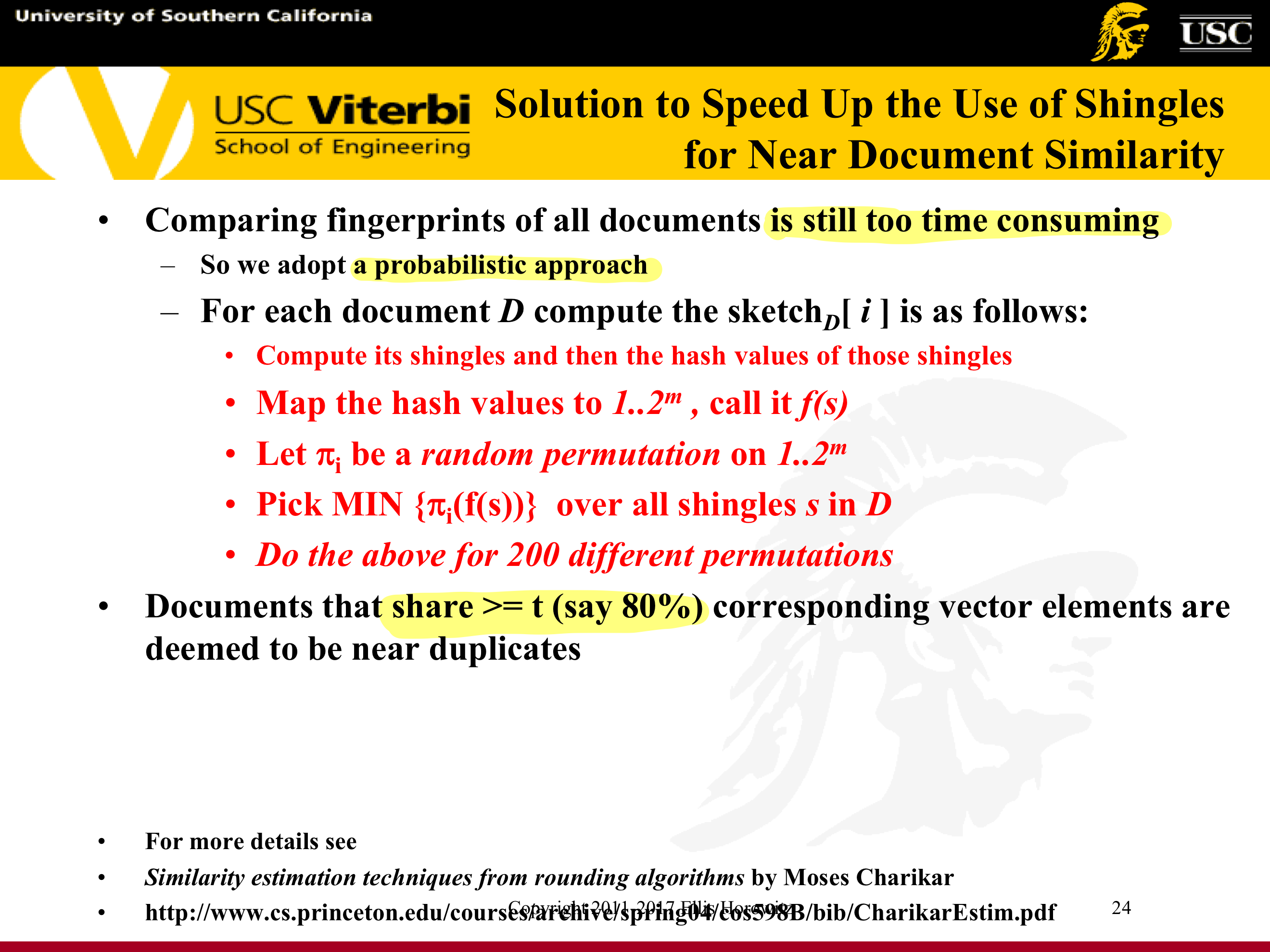
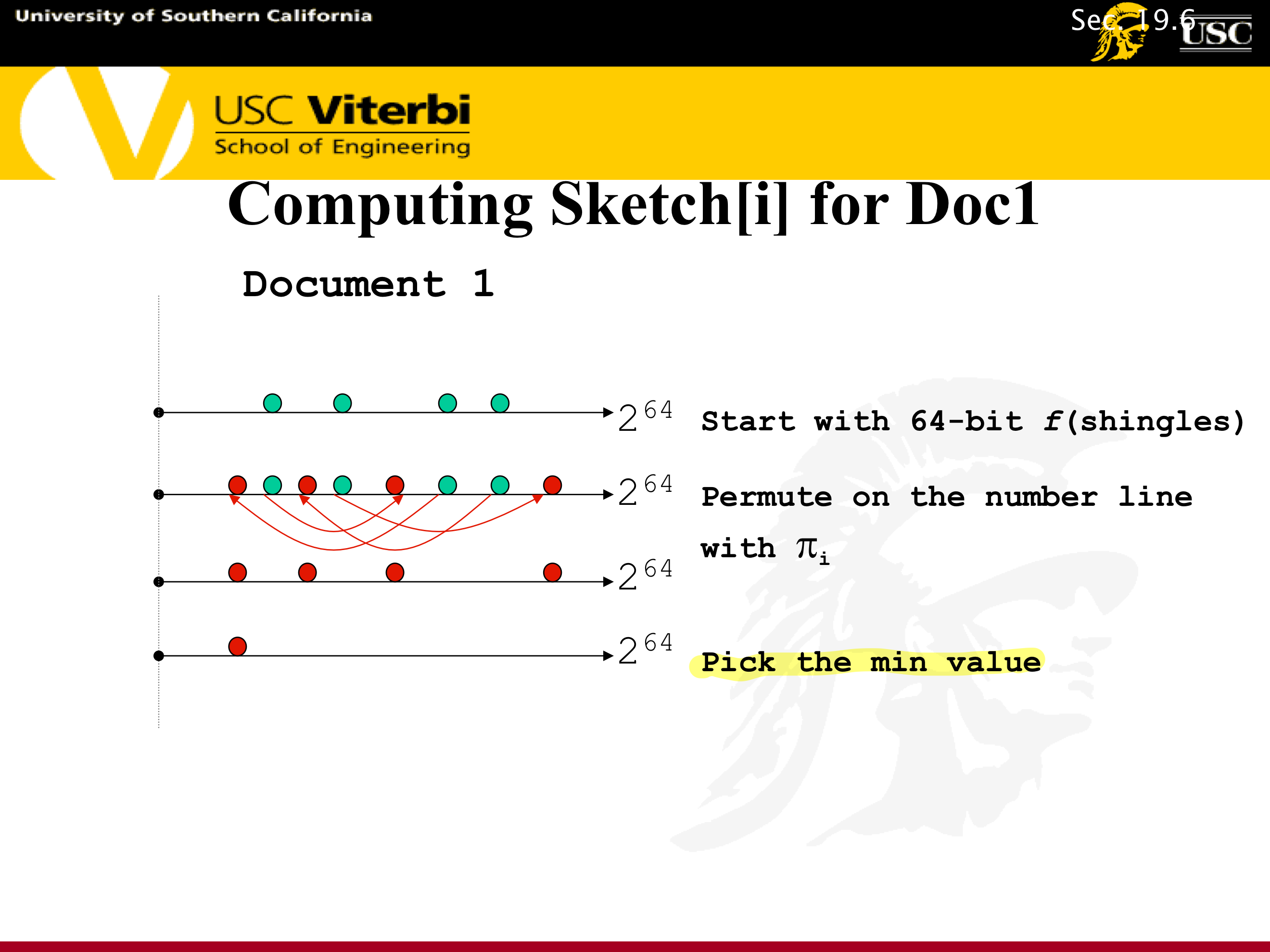
- Produce fingerprints and test for similarity
- Treat web documents as a set of features, constituting an n-dimensional vector, and transform this vector into an f-bit fingerprint of a small size
- Use Simhash and Hamming Distance to compute the fingerprint
- Compare fingerprints and look for a difference in at most k bits – E.g. see Manku et al., WWW 2007, Detecting Near-Duplicates for Web Crawling, http://www2007.org/papers/paper215.pdf
- Compute Shingles and test for similarity
- Compute w-shingling
- Broder et al., WWW 1997, Finding Near Duplicate Documents
7.1.5.4. General Paradigm
- Define a function
fthat captures the contents of each document in a number- E.g. hash function, signature, or a fingerprint
- Create the pair
<f(doci), ID of doci>for alldoci - Sort the pairs
- Documents that have the same f-value or an f-value within a small threshold are believed to be duplicates
7.1.5.5. General Properties of Distance Measures
A distance measure must satisfy 4 properties :
- No negative distances
D(x,y) = 0iff x=yD(x,y) = d(y,x)symmetricD(x,y) <= d(x,z) + d(z,y)triangle inequality
There are several distance measures that can play a role in locating duplicate and near- duplicate documents
Euclidean distance
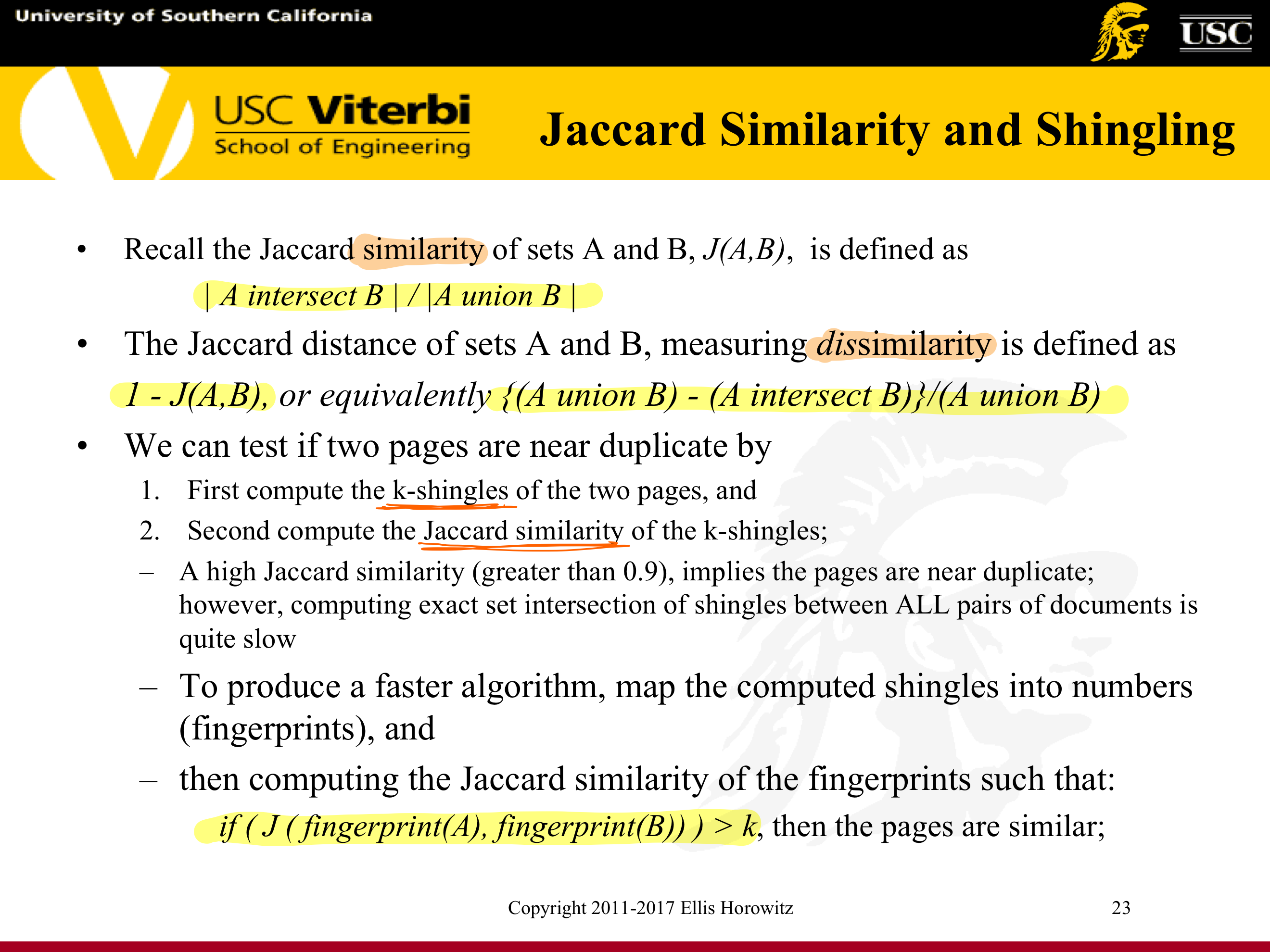
Jaccard distance or 1 minus the ratio of the sizes of the intersection and union of sets x and y
Cosine distance the cosine distance between two points (two n element vectors) is the angle that the vectors to those points make; in the range 0 to 180 degrees
Edit distance the distance between two strings is the smallest number of insertions and deletions of single characters that will convert one string into the other
Hamming distance between two vectors is the number of components in which they differ (usually used on Boolean vectors)
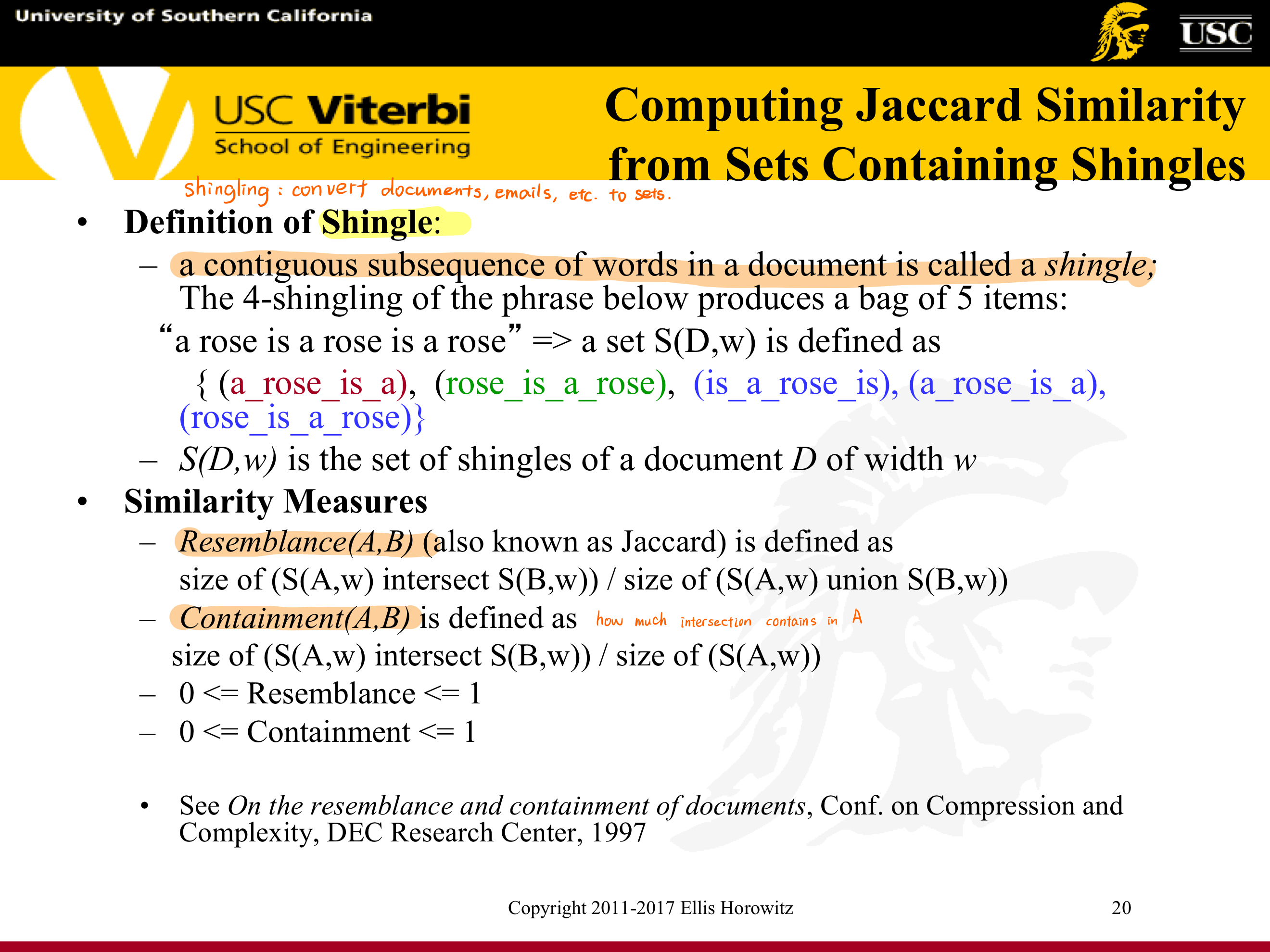
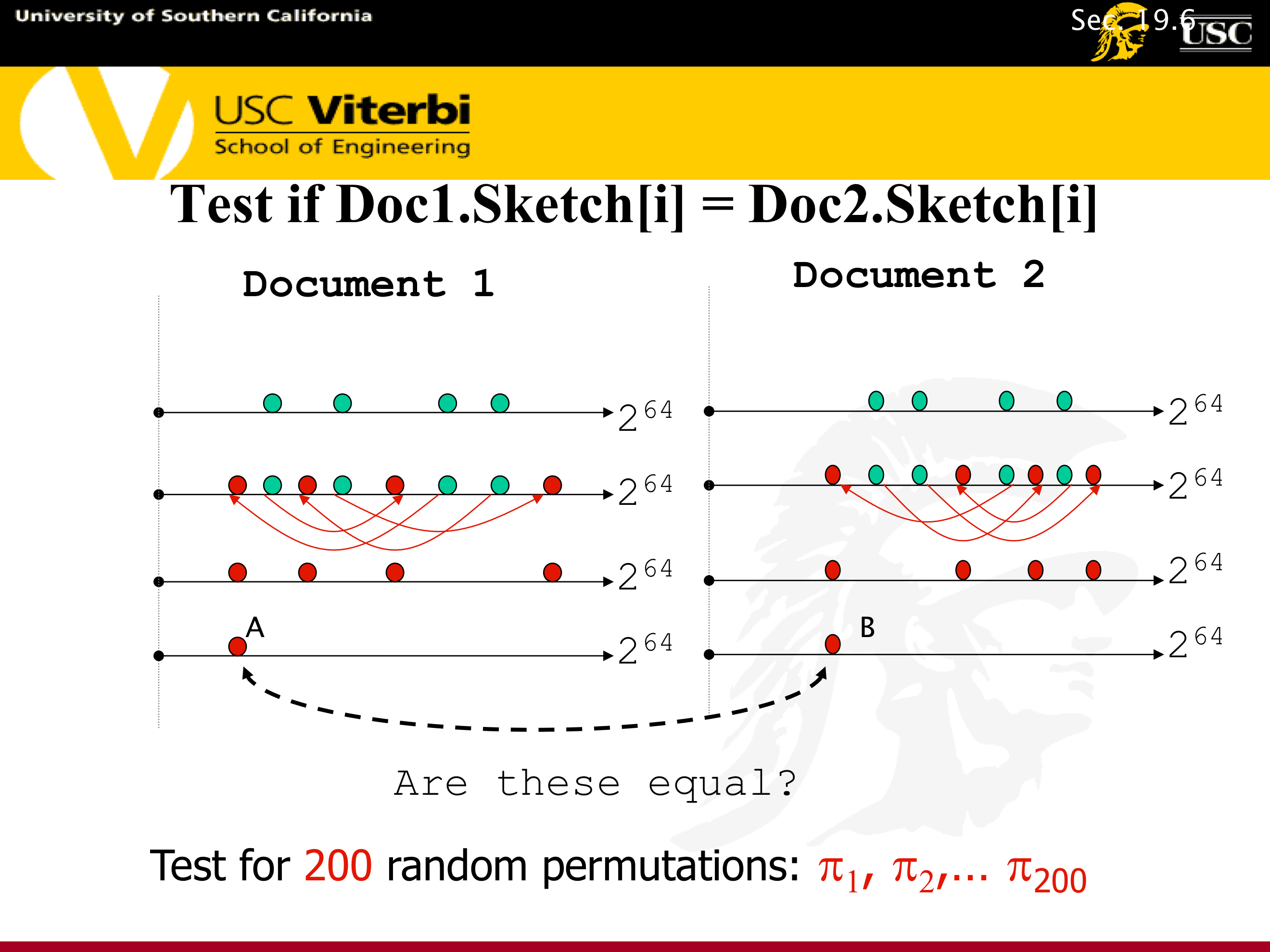
7.1.5.6. Computing Jaccard Similarity from Sets Containing Shingles
Definition of Shingle: a contiguous subsequence of words in a document is called a shingle;
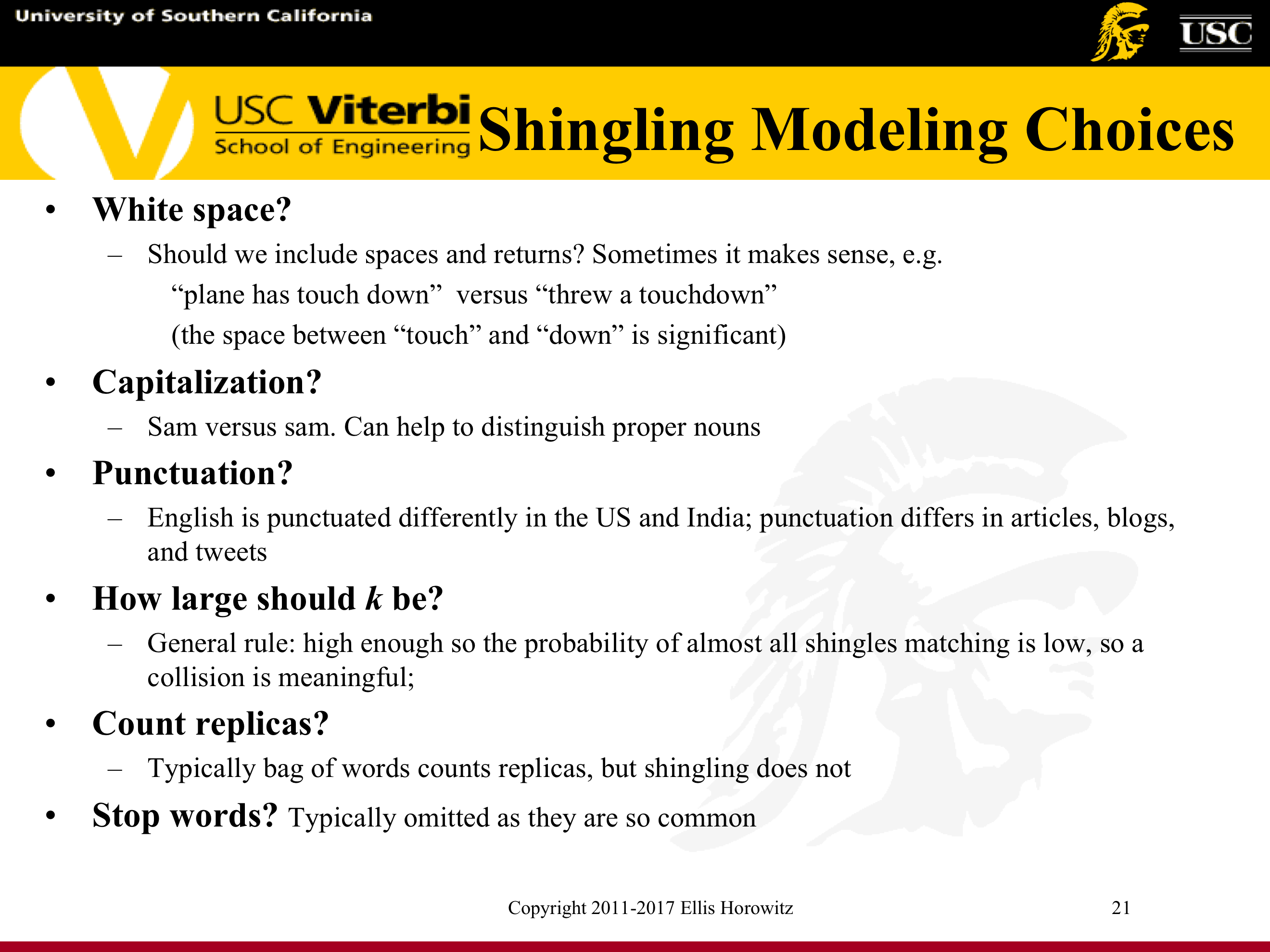
7.1.5.7. Shingling Modeling Choices
Shingling : convert documents, emails, etc. to sets
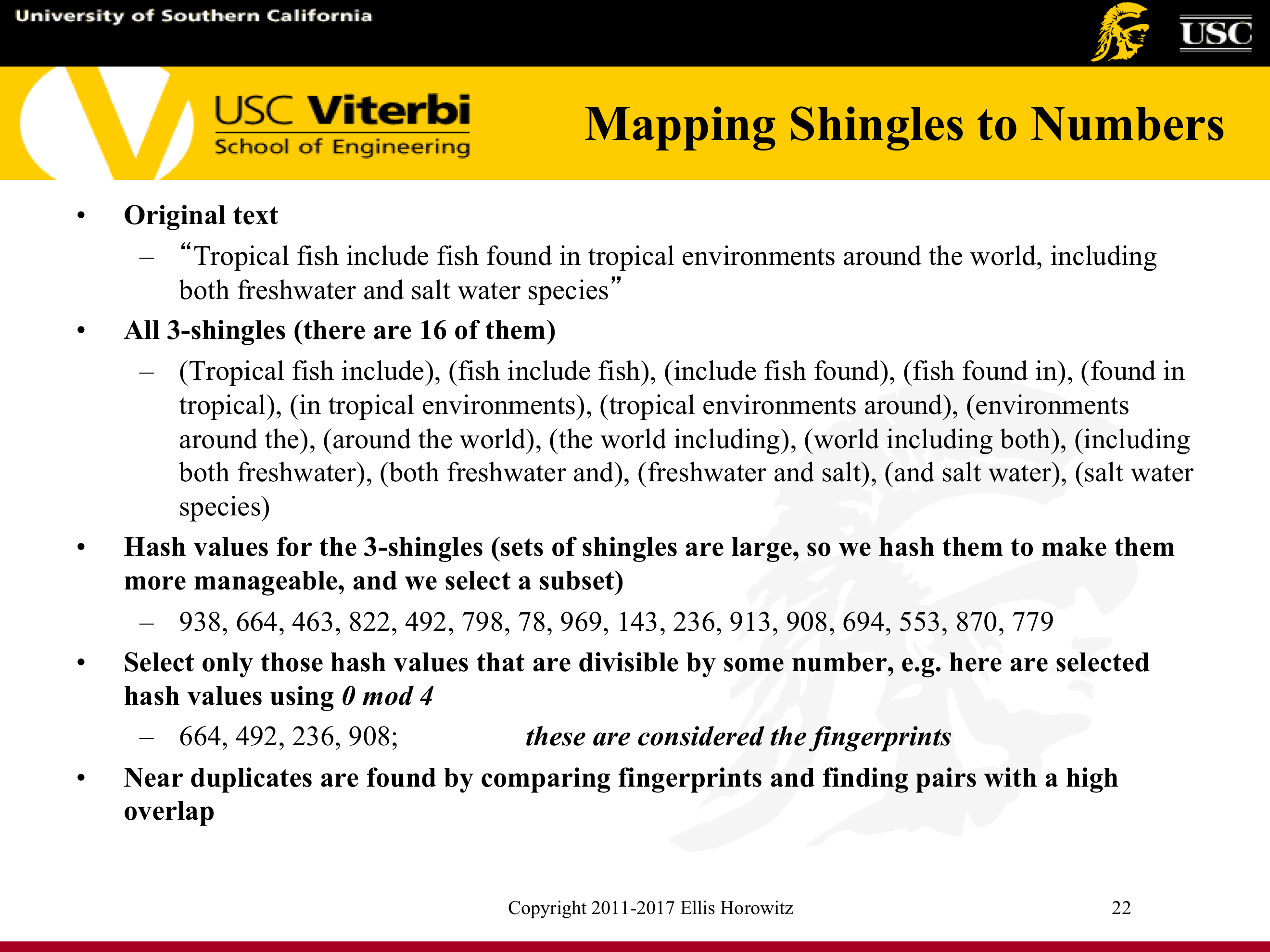
7.1.5.8. Mapping Shingles to Numbers

7.1.5.9. Simhash by Moses Charikar A Locally Sensitive Hash Function